Hip osteoarthritis (arthropathy) is a chronic progressive disease in which a degenerative dystrophic process occurs in the pelvic joint area. More precisely, the hyaline cartilage lining the femoral head and acetabulum is destroyed and the pelvic surfaces touch each other.
A second name for pathology is coxopathy of the hip.
Arthropathy of the hip: characteristics of the disease
For the most part, first-hand knowledge about hip arthropathy is in older adults (mainly women) who are at risk of developing the pathology after 45 years. This selective pathology arises from the peculiarities of women's pelvic structures and their direct involvement in the delivery process. In men, joint disease of the hip (hip disease) occurs mainly after the age of 65.
An important role in the pathogenesis of hip disease is the body's natural aging, when the most stressed joints in the bone begin to collapse.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by a number of infectious, traumatic, non-inflammatory diseases and combinations thereof. Initially, arthropathy manifests as pain and reduced motor activity in the pelvic area, but then its consequences become more severe - shortening of the affected limb.
Disease classification
The type of hip arthropathy depends on the characteristics of its development and the cause of its occurrence. There is usually post-traumatic arthropathy of the hip - it appears after an injury. The classification also includes the following types of arthropathy:
- stunting - due to stunted growth that occurs in childhood but is not cured;
- Static - associated with uneven loading of the pelvic region, which is associated with lesions of the feet, knees, ankles;
- Post-infection - occurs after various inflammatory diseases;
- Primary chronic - develops in older adults due to aging of the body.
Any type of disease can be referred to as "degenerative joint disease of the hip" because the pathology results in a disruption of the shape and appearance of the pelvic joints.
In addition, the disease is classified into 3 grades according to the severity of the changes, the symptoms of which are described below.
Causes of joint disease
Even without obvious prerequisites, signs of hip arthropathy can occur due to a natural degenerative process in the joint. It has narrow clearances while bearing huge and constant loads, so it wears out earlier than other products. Initially, blood circulation in the tissue is disturbed, so nutrients are delivered to the hyaline cartilage to a lesser extent. Metabolic processes are disturbed, cartilage dries out, and cracks form. In addition, the articular surface is quickly worn away, destroyed - arthropathy of the hip joint progresses. Symptoms appear faster if the body is under the influence of many stimuli:
- any harm;
- Physical labor, heavy physical exercise;
- spinal disorders, including curvature;
- flatfoot;
- Arthritis in the context of an infectious process;
- joint dysplasia metastasized in childhood;
- metabolic disease;
- excess weight;
- Rheumatism and other autoimmune diseases.
In the context of these factors, the disease progresses faster - 30-40 years later.
Symptoms of hip disease
Signs of hip arthropathy largely depend on its extent. During pathology, three degrees (stages) are distinguished:
- first level. Pain when the body is overloaded - after a long walk, run, a painful, dull feeling in the pelvic area (passed after a short rest). The pain does not radiate to the rest of the leg. Degree 1 hip deformity joints do not cause gait changes and muscle function is adequate. By the end of the phase, there may be a slight limitation of leg movement;
- second degree.In this case, the pain in the hip joint becomes more pronounced. Pain from light exertion and discomfort at night after workday. Pain at night, while resting. Crunching sound, rubbing at the joints. If a person walks for a long time, a swaying motion can be noticed in the gait. Putting your shoes on becomes difficult, put your feet aside;
- Three degrees.The work of the pelvis is severely impaired (primary arthropathy, both joints are affected, other types, usually only one). The pain in the groin is constant, unbearable and it gives the knee. Thigh muscle atrophy. The legs are shortened, so one moves with crutches and crutches.
Later, rigidity occurs, in which movement becomes impossible at all.
Disease diagnosis
What is hip hip disease, how severe is it, and how is it treated? All issues should be resolved after diagnosis. Although the primary method of diagnosis is radiography, patients need to consult a few narrow specialists and get tested. This will help find the cause of the disease and take action. Therefore, osteochondrosis, flat feet, urological and gynecological infections may cause hip joint disease, and their treatment will help stop the destruction of the bone and joint.
As far as making an accurate diagnosis and setting the arthropathy, all the changes can be seen perfectly in the picture - X-ray or CT (MRI):
- The first degree is that the gap is slightly narrowed and marginal osteophytes appear;
- Grade II - 50% reduction of the joint space, osteophytes on the outside and inside of the space, deformity of the femoral head, usually - inflammatory changes in the tissues near the joint bones;
- The third degree is severe joint deformity with large osteophytes and sclerotic areas.
Treatment of joint disease
Conservative treatment
Ointments, creams, and tablets for hip joint disease are only helpful in the first stage of the disease. Drugs can fully restore cartilage, and it is important to start treatment early. NSAIDs, corticosteroids, chondroprotectants, hyaluronic acid-based drugs, muscle relaxants are commonly used. They also practice massage, sports therapy and therapeutic exercises.
In the second stage, it is necessary to link physiotherapy and mechanical methods affecting the joints. These include range hoods, UHF, magnetic therapy, shock wave therapy, ultrasound, lasers, induction heat, electrophoresis. Folk remedies for the hip joint, like topical medicine, are only secondary, and the main treatment method should be medicine.
Be sure to follow a diet for hip hip disease, which is required to normalize metabolism and improve cartilage nutrition.
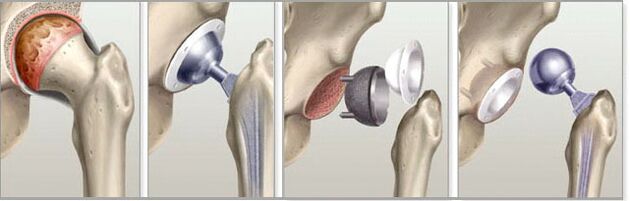
Joint prosthesis
The third stage of the disease can only be treated by surgery. Patients are advised to undergo joint replacement surgery, or arthroplasty. The surgeon cuts off the head of the femur, inserts a metal needle into the incision, and attaches the artificial head to the incision. After a long period of rehabilitation and exercise treatment, the hip joint function will be completely normal. The doctor will give a positive answer to the question of whether the hip joint can be squatted.
prevent disease
To prevent hip joint disease, exercise and a healthy lifestyle must come to the fore. Overloading of the joints is impossible, but it is necessary to eliminate the lack of power. Suitable for walking, swimming, skiing, elliptical trainer. Losing weight and eating right are also important.

Prevention of hip arthropathy is also based on early treatment of any bruises, injuries affecting the pelvis and spine. In childhood, all congenital joint pathologies should also be eliminated.
Answers to popular questions
- Who comes into contact with arthritis? There is no clear answer to the question of which doctor treats hip osteoarthritis. Of course, it is initially recommended to contact a surgeon, traumatologist or orthopaedic surgeon, depending on the clinic's capabilities. In specialty centers, arthrologists deal with pelvic joint problems, but such narrow specialists are not always available.
Depending on the cause of the disease, in the future, you will have to simultaneously apply for and receive treatment under the supervision of a rheumatologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist and some other doctors;
- Can arthritis be cured? The disease is chronic and it is impossible to completely eliminate it, especially since the main cause is aging. But if you go to the doctor when you have first-degree hip arthropathy, you can heal all existing changes and then prevent rapid progression. In subsequent stages, all existing pathological changes can be stopped and repaired, and a normal life can be achieved due to regular treatment. Only arthroplasty can save a joint from arthropathy, but it also has many disadvantages - from the need for regular replacement of prostheses to postoperative complications - pain, thrombosis, infection;
- When is topical treatment sufficient and under what circumstances can a doctor visit be avoided? Any ointment can only slightly improve blood microcirculation in the joint area and also relieve pain, but it has no therapeutic effect. In addition, this joint is deep and difficult for active substances to penetrate. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a doctor at any stage of the disease, regardless of the severity of the presentation. Only in the early stages can the disease be stopped with "a small amount of blood" without surgery.
Hip arthropathy is a disabling pathology that renders a person paralyzed and unable to walk.
The only way to prevent the development of such problems is to start conservative treatment at stage 1-2 of the disease and do not forget to conduct regular and comprehensive courses.


















